The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that has escalated in recent years, leaving many Americans grappling with the dream of homeownership. With the average price of a new single-family home more than doubling since 1960, factors such as labor costs and material shortages have become alarmingly apparent. However, a critical underlying cause that can no longer be ignored is the impact of NIMBY land-use policies, which stifle construction productivity and innovation. Compounded by a housing market decline influenced by stringent real estate regulations, many potential buyers are being pushed out of the market entirely. To tackle this crisis, a comprehensive understanding of American housing trends and the historical context of these regulations is essential to pave the way for more affordable housing solutions.
Addressing the housing affordability dilemma requires exploring various terms and concepts that highlight its complexity. The current predicament of escalating home prices has led to a significant barrier for many prospective homeowners seeking affordable living options. This urgent situation, often characterized by restrictive land-use policies and shifting real estate dynamics, has hindered the ability to construct new homes efficiently. Furthermore, declining productivity within the construction industry, compounded by regulatory challenges, underscores the pressing need for innovation in housing solutions. As we navigate these interconnected issues, it is crucial to examine the broader implications for society and the economy.
The Impact of NIMBY Land-Use Policies on Construction Productivity
NIMBY, or ‘Not In My Back Yard,’ land-use policies have emerged as a significant barrier to housing development across the United States. These policies, often rooted in community resistance to high-density housing or large construction projects, have contributed to a stifling regulatory environment. This has led to smaller, less efficient construction projects that fail to take full advantage of economies of scale. Consequently, the overall productivity within the construction industry has plummeted, as builders are forced to navigate an increasingly complex web of regulations that inhibit innovation and growth.
The restriction on large developments has profound implications on the U.S. housing market, specifically in relation to the pricing and availability of homes. When builders can only pursue smaller projects, they derive fewer housing units from their labor, leading to increased costs per unit. As demand continues to rise, the restriction placed by NIMBY policies contributes directly to the ongoing housing affordability crisis, taking homeownership out of reach for many Americans and exacerbating socioeconomic divides.
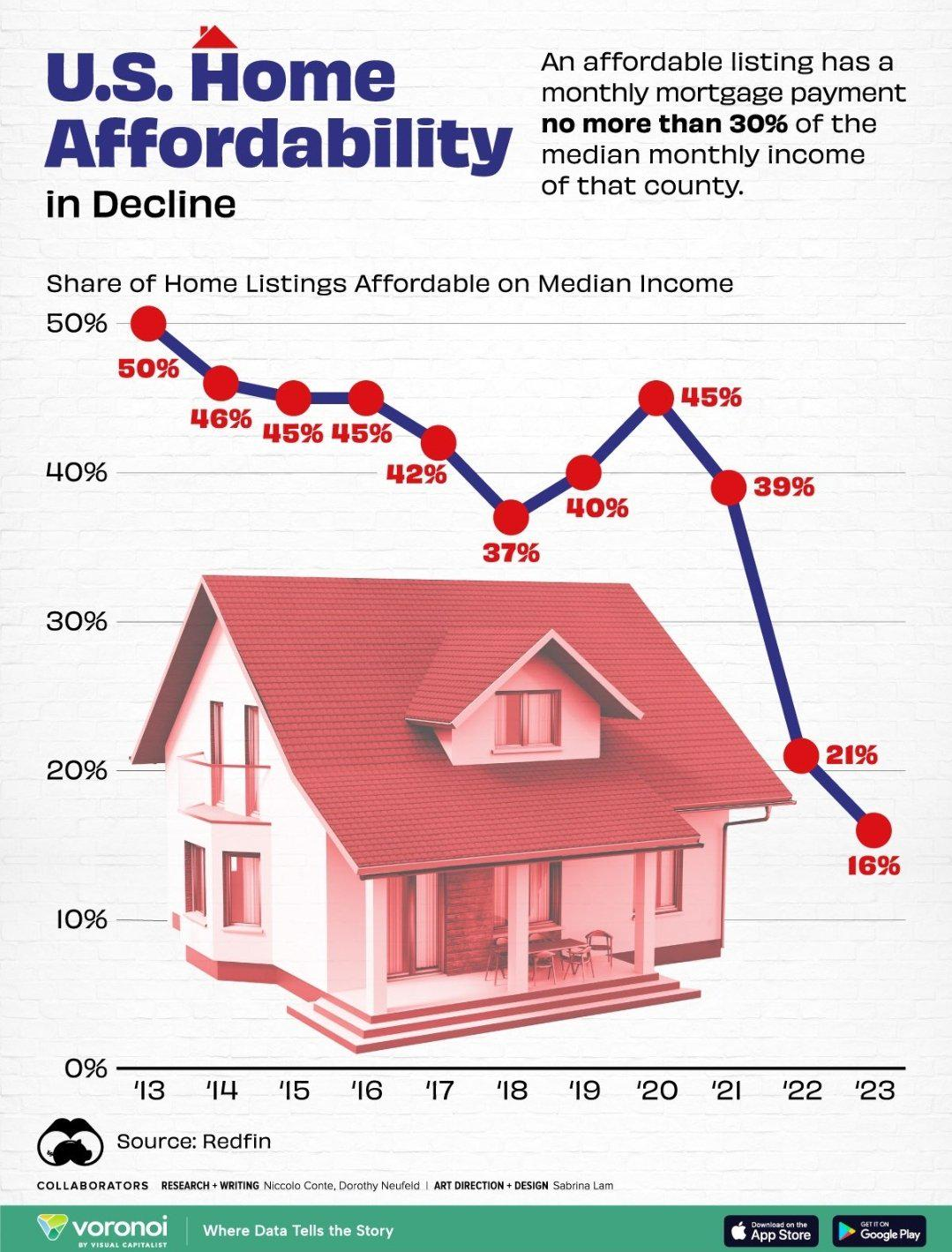
Housing Affordability Crisis: Causes and Consequences
The current housing affordability crisis in America is a multifaceted issue rooted in decades of economic and regulatory changes. Over recent years, the price of homes has skyrocketed, largely due to rising labor costs, materials expenses, and the significant influence of land-use regulations. With home prices now consistently outpacing wage growth, many Americans are struggling to achieve the dream of homeownership. This crisis has made it increasingly difficult for first-time buyers, young professionals, and low-income families to secure housing, pushing many into rental markets that are also experiencing considerable price hikes.
The implications of this crisis extend beyond individual challenges, affecting entire communities and the economy at large. Households burdened by housing costs often have less disposable income to spend on goods and services, which stifles local economies and can impede job creation. Furthermore, the demographic shift towards renting indicates a trend of wealth consolidation among older generations who continue to own homes, while younger generations find themselves trapped in a cycle of escalating rent payments without the opportunity to build equity. This intergenerational wealth transfer has further entrenched disparities within the housing market.
Exploring American Housing Trends: Historical and Present Analysis
Housing trends in America have undergone significant transformations over the past several decades, reflecting broader changes in economic conditions and societal norms. In historical contexts, periods of rapid urbanization and economic growth facilitated booms in housing construction, with large-scale developments meeting the burgeoning demand for affordable homes. However, since the 1970s, there has been a marked decline in construction productivity due to increasing regulations and NIMBY land-use policies that obstruct larger projects. This shift has resulted in smaller home offerings, which cannot keep pace with the needs of a growing population.
Today, American housing trends signal a move towards increased complexity and additional challenges for potential homeowners. The construction industry is witnessing the emergence of boutique developments tailored to the unique desires of small communities instead of larger, more affordable housing units. This trend not only limits access to affordable options but also reinforces a cycle of exclusivity and wealth concentration, as the housing supply remains disproportionately skewed towards high-value markets. Continual scrutiny and adaptation of these trends are essential for fostering a more equitable housing landscape.
Construction Productivity and Its Decline in the U.S. Housing Sector
The decline in construction productivity within the U.S. housing sector has raised concerns among economists and policymakers alike. Research indicates that the productivity of construction has dropped significantly since the turn of the 1970s, coinciding with an increase in local land-use regulations that have complicated the building process. This stagnation has severe consequences for housing affordability and availability, as builders struggle to meet demand with increasingly impractical and time-consuming project requirements. As a result, fewer homes are built, leading to supply shortages amidst rising populations.
It is pertinent to recognize that this decline in productivity does not reflect a lack of innovation or capabilities within the construction sector itself but rather highlights the detrimental impact of regulation. While other industries, like manufacturing, have advanced through new technologies and efficiency measures, the construction sector finds itself constrained by regulations that hinder large-scale developments. To combat this issue, addressing the tensions between community concerns and housing development needs is crucial for restoring productivity and diminishing the current housing affordability crisis.
Real Estate Regulation: Understanding Its Role in the Housing Market
Real estate regulation plays a pivotal role in shaping the housing market dynamics in the United States. By implementing zoning laws, building codes, and land-use policies, local governments aim to manage growth, protect the environment, and maintain community standards. However, when these regulations become overly restrictive or complex, they often result in unintended consequences that restrict construction productivity. High compliance costs and delays can deter potential developers from initiating new projects, exacerbating the existing challenges in housing supply and affordability.
Moreover, the current regulatory landscape reflects a growing tension between community interests and the need for increased housing supply. While it is essential to consider residents’ concerns regarding development, it is equally important to provide ample opportunities for builders to meet demand. Striking a balance between these competing interests can foster a more adaptable real estate market, encouraging growth and innovation while addressing the pressing concerns of community members and ultimately easing the housing affordability crisis.
Addressing the Housing Crisis Through Policy Reform
Addressing the ongoing housing crisis requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on policy reform at various levels. Streamlining the approval processes for housing projects by reducing bureaucratic hurdles can significantly enhance construction productivity. Additionally, reconsidering land-use regulations to allow for larger scale developments could incentivize builders to invest in housing projects that are more economically viable and cater to the needs of the community. A shift towards flexible zoning that accommodates high-density developments and mixed-use spaces may provide solutions to the housing scarcity problem.
Furthermore, fostering public-private partnerships can be instrumental in developing innovative solutions for affordable housing. Collaborating with private developers to create housing that aligns with community needs can lead to shared benefits and mutual investment. By actively engaging stakeholders, including residents and housing experts, policymakers can cultivate a more inclusive dialogue around housing development that prioritizes both affordability and community harmony. Comprehensive reform will ultimately be essential in redirecting the trajectory of the housing market and alleviating the pressures of the affordability crisis.
The Future of Housing: Innovations and Sustainable Solutions
Looking towards the future, the housing market must embrace innovation to overcome the current challenges of affordability and access. Advancements in technology, particularly in construction methods such as modular and prefabricated building, offer exciting prospects for reducing costs and construction times. By harnessing modern techniques, builders can deliver high-quality homes at lower prices, which could provide a significant boost to housing supply essential for a robust recovery in the U.S. housing market.
Sustainability will also play a crucial role in shaping the future of housing. As environmental concerns become increasingly salient, integrating eco-friendly building practices can enhance both the livability and efficiency of new constructions. Initiatives promoting energy-efficient designs and sustainable materials can create homes that not only minimize environmental impact but also reduce long-term operating costs for homeowners. By combining innovative practices with a focus on sustainability, the housing sector can address present challenges while paving the way for a more resilient future.
Intergenerational Wealth Transfer in Housing: Understanding the Implications
The dynamics of intergenerational wealth transfer in housing present significant implications for economic equity and social mobility in America. As older generations accumulate wealth through homeownership, younger demographics often struggle to enter the market due to skyrocketing prices and diminished savings capabilities. This wealth disparity shapes not only individual opportunities but also broader economic trends, as younger generations are less likely to invest in real estate, thus perpetuating cycles of wealth inequality. Understanding these implications is essential for addressing the ongoing housing affordability crisis.
Efforts to promote policies that support first-time homebuyers or encourage alternative ownership models can help bridge this gap. For instance, initiatives designed to foster affordable housing development or provide financial incentives for young families can create pathways to homeownership that were previously unavailable. By facilitating access to housing for younger generations, we can foster a more equitable distribution of wealth and ensure that future economic growth is inclusive and sustainable.
Community Involvement: A Key to Sustainable Housing Solutions
Community involvement is a fundamental aspect of developing sustainable housing solutions. Encouraging civic engagement in discussions surrounding housing policies can lead to outcomes that align with the needs and desires of local residents. Community members often possess valuable insights and priorities that, when addressed, can foster a more collaborative approach to housing development. By enabling open dialogue between builders, policymakers, and residents, communities can advocate for projects that enhance livability and ultimately contribute to resolving the housing affordability crisis.
Moreover, engaging communities in the planning stages of housing developments can help mitigate the resistance often associated with NIMBY attitudes. When residents feel that their voices are heard and their concerns are taken into consideration, they are more likely to support new projects that bolster the economy and provide necessary housing. Building this collaborative atmosphere can be a significant step toward creating homes that reflect shared values while fostering sustainable growth and community cohesion.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NIMBY land-use policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY land-use policies, or ‘Not In My Backyard’ regulations, often restrict the development of new housing projects. These controls can lead to decreased construction productivity by making it difficult for builders to construct large-scale developments, which are essential for mass-producing affordable homes. The result is a significant escalation in housing costs, contributing to the current housing affordability crisis faced by many Americans.
What role does construction productivity play in the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity has been on the decline since the 1970s, largely due to stringent land-use regulations like NIMBY policies. This decrease in efficiency hinders builders’ ability to keep housing prices manageable. As a result, the ongoing housing affordability crisis is exacerbated by a construction sector that struggles to innovate and scale up production to meet rising demand.
How has the housing market decline affected American housing trends?
The housing market decline, driven by escalating costs from NIMBY regulations, has shifted American housing trends towards smaller, more custom-built homes rather than efficient, large-scale developments. This shift limits the availability of affordable housing options, further entrenching the housing affordability crisis and making homeownership unattainable for many.
What impact do real estate regulations have on the housing affordability crisis?
Real estate regulations, particularly those stemming from NIMBYism, directly impact the housing affordability crisis by increasing costs and creating barriers to entry for builders. These regulations often complicate the development process, leading to fewer new homes being built and exacerbating the already critical lack of affordable housing.
What are some recent American housing trends related to the housing affordability crisis?
Recent American housing trends indicate a significant decrease in the production of large-scale housing projects due to NIMBY policies. This trend has led to a reliance on smaller, bespoke builds that are not cost-effective, further driving the housing affordability crisis as median home prices outpace average incomes, making it harder for many Americans to achieve homeownership.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Housing prices have more than doubled since 1960, contributing to a housing affordability crisis. |
| Land-use policies, specifically NIMBYism, restrict builders and inflate home costs. |
| Construction productivity has decreased significantly since 1970, while other sectors continue to grow. |
| The size of housing projects has declined, leading to less innovation and efficiency in the building sector. |
| Large-scale builders produce housing units more efficiently than smaller firms, but their market share has fallen. |
| Intergenerational wealth transfer in housing has left younger Americans with significantly less housing wealth. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a growing concern in America, as more and more individuals and families find the prospect of homeownership increasingly unattainable. This crisis stems from a combination of factors, notably the impact of stringent land-use regulations, known as NIMBYism, which stifles innovation and productivity within the construction sector. These regulations have led to higher costs, smaller projects, and a notable decline in construction efficiency since the 1970s. Moreover, the dramatic shift in housing wealth distribution over the decades poses significant challenges for younger generations, making it critical for policymakers to address these issues to ensure a more accessible housing market for all.