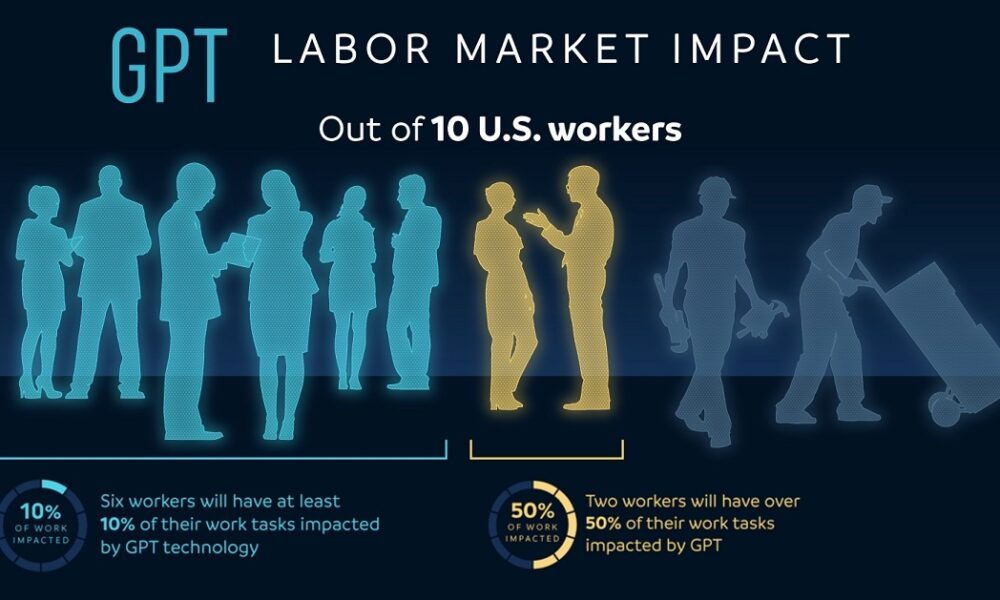
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly pronounced as researchers delve into the ways artificial intelligence job disruption is reshaping employment dynamics. A recent study by Harvard economists reveals how technological advancements have historically altered the workforce landscape, reminiscent of previous employment trends technology has introduced. While past decades showed a striking stability in the labor market, a significant shift since 2019 indicates that new AI-driven trends are emerging. Occupational churn analysis within this context uncovers vital insights, particularly concerning the declining share of low-wage jobs alongside a surge in higher-skilled positions. This transformation emphasizes the need to understand automation effects on jobs, as AI not only enhances productivity but also brings about uncertainty regarding employment stability across various sectors.
As we navigate the evolving terrain of professional employment, the advent of intelligent systems and automation tools makes it essential to consider their influence on job availability. The emergence of automation technology is prompting a profound reassessment of traditional roles within industries, leading to a restructuring of workforce requirements and skillsets. With a focus on how machine learning and robotic solutions contribute to historical labor market changes, it becomes evident that the modern economy is experiencing unprecedented transformations. The ongoing occupational evolution calls for a comprehensive approach to understanding labor dynamics and preparing for the potential implications of such rapid technological integration. Ultimately, the interplay between AI and the workforce invites critical conversations about the future of work and the adaptability of human skills in an increasingly automated world.
The Role of AI in Modern Labor Market Transformations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a formidable force that is reshaping the labor market, prompting discussions on how it might alter employment trends. As highlighted in the study by Deming and Summers, AI is not just another technological advancement; it’s creating a paradigm shift similar to historical labor market changes brought about by innovations in communication and manufacturing. The impact of AI spans various sectors, pushing organizations to rethink their workforce strategies in light of the accelerating pace of automation.
The disruption caused by AI is evidenced by a noteworthy trend in occupational churn, where certain job categories are witnessing substantial declines while others, notably those that require technical skills, are on the rise. This growing divide signals a shift toward higher-skilled job requirements, indicating that workers may be left behind if they do not adapt. The study’s findings suggest that AI could be the catalyst for a new wave of employment polarization, altering the landscape of job availability in ways that mirror past technological upheavals.
Understanding Occupational Churn and Job Polarization
Occupational churn, defined as the constant movement of jobs within the labor market, provides valuable insight into how employment trends evolve in response to technology. According to the recent study, the U.S. labor market underwent significant stability for nearly three decades before experiencing a new phase of volatility spurred in part by AI advancements. This phenomenon highlights the historical patterns of job demand and the ways new technologies have historically disrupted established employment categories, forcing workers to continuously upskill.
The barbell-shaped implication of job polarization illustrates a growing gap where low-paid and high-paid jobs proliferate, leaving a void in middle-income positions. This shift corresponds with the recent emergence of AI-driven jobs that necessitate advanced training and expertise. The analysis suggests that as technology continues to evolve, the nature of work will similarly transform, demanding a workforce that can adapt to these changes while also grappling with potential job displacement in less skilled sectors.
Historical Labor Market Changes and Predictions for the Future
Examining historical labor market changes gives context to the current situation where AI is becoming ubiquitous across industries. Past technological advancements have consistently led to dramatic shifts in job types and the skills required for employment. The economist’s analysis reveals that future predictions should account for the potential acceleration of these changes, driven partly by AI, which may render considerable segments of the workforce obsolete. Thus, understanding these historical trends is critical for anticipating future job market dynamics.
As we stand on the brink of another technological revolution, the implications of AI’s integration into the workforce are vast. With projections of continued job displacement, particularly in occupations with repetitive tasks, businesses and educational institutions alike must prepare for a future where adaptability and continuous learning are paramount. The persistence of AI’s influence in the labor market implies that without proactive strategies, many workers may find themselves on the wrong side of technological progress.
Automation Effects on Jobs: Insights from Recent Studies
The effects of automation on jobs have been a topic of concern for decades, particularly with the rising presence of AI in the workplace. Recent studies show a significant decline in low-paid service jobs, raising questions about the availability and security of these employment opportunities as automation technologies advance. This trend, coupled with the findings of the labor market analysis, underscores the critical need for understanding how automation intersects with current job roles.
As automation reshapes traditional employment landscapes, it is increasingly clear that certain sectors will experience dramatic shifts, leading to job loss in specific areas. For instance, retail and service industries are already observing declines in job availability, mainly attributed to automation. This evolving context demands that businesses rethink their operational models and that workers equip themselves with the skills necessary to thrive in an environment where AI and automation play pivotal roles.
The Impact of AI on Job Growth in STEM Fields
As research indicates a shift towards job growth in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, the influence of AI becomes increasingly prominent. The analysis reflects a rising demand for skilled professionals in technical roles, with STEM jobs increasing from 6.5% to nearly 10% of the overall job market. This is a significant growth indicating that workers with the right skills are likely to find ample job opportunities in the booming tech sector.
The rise in demand for STEM occupations highlights the essential role of education and training systems in preparing the workforce for an AI-driven future. Educational institutions may need to adapt curricula to focus more on technical skills that align with the evolving job landscape. As companies ramp up their investments in AI technologies, the emphasis on preparing students for careers in these areas may dictate the future workforce’s success and collective capability to navigate emerging technological challenges.
COVID-19 and Its Role in Accelerating Job Market Changes
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated many trends already in motion within the labor market, particularly those related to automation and the adoption of technology. As companies were forced to adapt to remote work and health-related restrictions, it became clear that many traditional job roles were not only at risk of being automated but could also be phased out altogether. This drastic shift has implications for employment trends, especially in low-wage sectors that are now experiencing prolonged periods of decline.
Moreover, the pandemic has sparked a reevaluation of worker safety and operational efficiency, further pushing companies toward AI-driven solutions. Consequently, businesses that had previously resisted automation have now found it indispensable for survival. The research illustrates that while the pandemic introduced immediate disruptions, it also laid the groundwork for long-term changes in how work is viewed in the economy, particularly regarding the necessity for technology integration.
AI and the Future of Knowledge Work
The nature of knowledge work is also shifting as AI becomes more integrated into various industries. With automation and intelligent algorithms poised to redefine tasks traditionally handled by humans, knowledge workers face the challenge of adapting to new operational realities. The research suggests that as AI tools become commonplace, companies may expect higher productivity from workers, who will need to leverage these technologies to maintain their relevance in the workforce.
This evolving landscape implies that knowledge workers must now not only focus on their domain expertise but also on developing skills related to AI and data analytics. The necessity for workers to continually evolve and adapt to technological advancements will likely determine their career longevity and overall job satisfaction. Those who embrace the integration of AI into their workflows may find themselves at a distinct advantage in the changing job market.
Preparing for the Future: Skill Development in an AI-Driven World
As AI’s dominance in the labor market continues to grow, the emphasis on skill development becomes critical for current and future employees. Workers in every sector should cultivate a mindset of continuous learning, particularly in areas that AI is enhancing or transforming. By focusing on acquiring skills related to technology, creativity, and interpersonal communication, workers can better prepare themselves for an evolving job landscape where traditional roles may undergo dramatic shifts.
Companies also play a significant role in fostering this environment by investing in training programs that align with technological advancements. By prioritizing skill development, organizations can ensure their workforce remains competitive and agile. The ultimate goal is to create a labor market where workers feel supported and equipped to thrive amidst the rapid changes brought about by AI, rather than being left behind in an increasingly automated world.
The Importance of Strategic Workforce Planning in the Age of AI
As AI becomes a central player in shaping the labor market, strategic workforce planning must evolve in tandem. Organizations need to anticipate changes driven by AI technologies and understand their potential impact on different job roles. This involves continuously assessing the current workforce’s skill sets and determining gaps that need to be filled as new technologies come into play. Strategic planning is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with job displacement and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Furthermore, implementing proactive workforce strategies can empower employees to transition into new roles that emerge from AI integrations, allowing for a smoother adaptation process. Companies that embrace workforce planning will not only enhance their operational efficiency but also support their employees in navigating the changing job landscape. This symbiotic relationship will be foundational for organizational success and employee satisfaction in an AI-driven future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting job disruption in the labor market?
AI is significantly impacting job disruption in the labor market by changing the demand for certain skills and professions. As highlighted in recent studies, including those by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, there has been a noticeable shift in job distribution, particularly favoring high-skilled, high-paid positions. This transformation is characterized by a decline in low-paid service jobs, influenced by automation and AI technologies.
What are the employment trends technology is causing in the U.S. labor market?
Employment trends technology is notably causing a rise in STEM jobs, with their share increasing from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% by 2024. This trend reflects the increasing need for advanced technological skills driven by AI and other innovations, while traditional roles in sectors like retail and low-paid services are witnessing significant declines.
How does historical labor market changes inform current views on AI impact?
Historical labor market changes provide essential context for understanding the current impact of AI. By analyzing over a century of occupational churn, researchers found that previous technological disruptions led to periods of stability and volatility. Recent data suggests that AI is introducing a new wave of disruption, particularly since 2019, altering job distributions and elevating demands for higher education and training.
What is occupational churn analysis and how does it relate to AI?
Occupational churn analysis looks at the shifts within professions in the labor market, measuring how technology, including AI, changes employment patterns. Recent studies show that while there was a stabilizing period, the current trend indicates increased volatility in job markets, particularly affecting lower-wage occupations while promoting high-skilled jobs driven by AI advancements.
What are the automation effects on jobs due to AI advancements?
The automation effects on jobs due to AI advancements are profound, with evidence showing a decline in traditional low-paid jobs, particularly in retail and services. Instead, there is growth in high-skilled jobs in STEM fields, reflecting AI’s role in reshaping job functions and driving firms toward investing in advanced technologies that optimize productivity.
| Key Trends | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization | The labor market is shifting away from job polarization, favoring high-skill, well-compensated roles. |
| STEM Job Growth | There has been a notable increase in STEM jobs, growing from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Jobs | Employment in low-paid service jobs has plateaued or declined, particularly since 2019. |
| Reduction in Retail Jobs | The retail sector has seen a 25% reduction in jobs, largely accelerated by the increase in e-commerce. |
Summary
The impact of AI on the labor market is increasingly evident, as highlighted by a recent study that underscores significant shifts in employment patterns. Researchers found that AI is driving changes in job types and availability, leading to a focus on high-skill opportunities while diminishing roles associated with low-paid jobs. With job polarization on the decline and STEM employment on the rise, the implications of AI are becoming paramount for future workforce dynamics. As industries adapt, professionals across sectors must be aware of AI’s transformative effects, equip themselves for the technological changes ahead, and embrace the potential for AI to enhance productivity while recognizing the risks of job displacement.